Appraisal management company (AMC): An institution operated independently of a lender that, once notified by a lender, orders a home appraisal.
Appraisal: An informed, impartial and well-documented opinion of the value of a home, prepared by a licensed and certifed appraiser and based on data about comparable homes in the area as well as the appraiser’s own walk-through.
Approved for short sale: A term that indicates that a homeowner’s bank has approved a reduced list price on a home and the home is ready for resale.
American Society of Home Inspectors (ASHI): A not-for-profit professional association that sets and promotes standards for property inspections and provides educational opportunities to its members. (i.e., Look for this accreditation or something similar when shopping for a home inspector.)
Attorney state: A state in which a real estate attorney is responsible for closing.
Back-end ratio: One of two debt-to-income ratios that a lender analyzes to determine a borrower’s eligibility for a home loan. The ratio compares the borrower’s monthly debt payments (proposed housing expenses, plus student loan, car payment, credit card debt, maintenance or child support
Buyer’s market: Market conditions that exist when homes for sale outnumber buyers. Homes sit on the market a long time and prices drop. Meaning = you win.
Cancellation of escrow: A situation in which a buyer backs out of a home purchase.
Capacity: The amount of money a home buyer can afford to borrow.
Cash-value policy: A homeowners insurance policy that pays the replacement cost of a home, minus depreciation, should damage occur.
Closing: A meeting during which ownership of a home is transferred from seller to buyer. The closing is usually attended by the buyer, the seller, both real estate agents
Closing costs: Fees associated with the purchase of a home that
Closing Disclosure (CD): A five-page document sent to the buyer three days before closing. This document spells out all the terms of the loan: the amount, the interest rate, the monthly payment, mortgage insurance, the monthly escrow amount and all closing costs.
Closing escrow: The final and official transfer of property from
Comparative Market Analysis (CMA): An in-depth analysis, prepared by a real estate agent, that determines the estimated value of a home based on recently sold homes of similar condition, size, features
Compliance agreement: A document signed by the buyer at closing, in which he or she agrees to cooperate if the lender needs to fix any mistakes in the loan documents.
Comps: Or comparable
Condo insurance: Homeowners insurance that covers personal property and the interior of a condo unit should damage occur.
Contingencies: Conditions written into a home purchase contract that protects the buyer should any issues arise with financing, the home inspection or other.
Conventional 97: A home loan that requires a down payment equivalent to 3 percent of the home’s purchase price. Private mortgage insurance, which is required, can be canceled when the owner reaches 80 percent equity.
Conventional loan: A home loan not guaranteed by a government agency, such as FHA or the VA.
Days On Market (DOM): The number of days a property listing is considered active.
Depository institutions: Banks, savings and loans and credit unions. These institutions underwrite as well as set home loan pricing in-house.
Down payment: A certain portion of the home’s purchase price that a buyer must pay. A minimum requirement is often dictated by the loan type.
Debt-to-income ratio (DTI): A ratio that compares a home buyer’s expenses to gross income.
Earnest money: A “security deposit” made by the buyer to assure the seller of his or her intent to purchase.
Equity: A percentage of the home’s value owned by the homeowner.
Escrow account: An account required by a lender and funded by a buyer’s mortgage payment to pay the buyer’s homeowners insurance and property taxes.
Escrow agent: A neutral third-party officer who holds all paperwork and funding in trust until all parties in the transaction fulfill their obligations as part of the transfer of property ownership.
Escrow state: A state in which an escrow agent is responsible for closing.
Fannie Mae: A government-sponsored enterprise chartered in 1938 to help ensure a reliable and affordable supply of mortgage funds throughout the country.
Federal Reserve: The central bank of the United States, established in 1913 to provide the nation with a safer, more flexible and more stable monetary and financial system.
Federal Housing Administration (FHA): A government agency created by the National Housing Act of 1934 that insures loans made by private lenders.
FHA 203(k): A rehabilitation loan backed by the federal government that permits
Foreclosure: A property repossessed by a bank when the owner fails to make mortgage payments.
Freddie Mac: A government agency chartered by Congress in 1970 to provide a constant source of mortgage funding for the nation’s housing markets.
Funding fee: A fee that protects the lender from loss and also funds the loan program itself. Examples include the VA Funding Fee and the FHA funding fee.
Gentrification: The process of rehabilitation and renewal that occurs in an urban area as the demographic changes. Rents and property values increase, culture changes and lower-income residents are often displaced.
Guaranteed replacement coverage: Homeowners insurance that covers what it would cost to replace property based on today’s prices, not the original purchase price, should damage occur.
Homeowner Association (HOA): The governing body of a housing development, condo or townhome complex that sets rules and regulations and charges dues and special assessments that are used to maintain common areas and cover unexpected expenses respectively.
Home equity loan: A lump-sum loan that allows the homeowner to use the equity in his or her home as collateral. The loan places a lien against the property and reduces home equity.
Home inspection: A non-destructive visual look at the systems in a building. Inspection occurs when the home is under contract or in escrow.
Homeowners insurance: A policy that protects the structure of the home, its contents, injury to others and living expenses should damage occur.
Housing ratio: One of two debt-to-income ratios that a lender analyzes to determine a borrower’s eligibility for a home loan. The ratio compares total housing cost (principal, homeowners insurance, taxes
In escrow: A period of time (30 days or longer) after a buyer has made an offer on a home and a seller has accepted. During this time, the home is inspected and appraised and the title searched for liens, etc.
Jumbo loan: A loan amount that exceeds the Fannie Mae/Freddie Mac limit, which is generally $425,100 in most parts of the United States.
List price: The price of a home, as set by the seller.
Loan estimate: A three-page document that is sent to an applicant three days after he or she applies for a home loan. The document includes loan terms, monthly payment
Loan-to-value ratio (LTV): The amount of the loan divided by the price of the house. Lenders reward lower LTV ratios.
Market value coverage: Homeowners insurance that covers the amount the home would go for on the market, not the cost to repair, should damage occur.
Mechanic’s lien: A hold against a property, filed in the county recorder’s office by someone who’s done work on a home and not been paid. If the homeowner refuses to pay, the lien allows a foreclosure action.
Mortgage broker: A licensed professional who works on behalf of the buyer to secure financing through a bank or other lending institution.
Mortgage companies: Lenders who underwrite loans in-house and fund loans from a line of credit before selling them off to a loan buyer.
Mortgage interest deduction: Mortgage interest paid in a year subtracted from annual gross salary.
Mortgage interest rate: The price of borrowing money. The base rate is set by the Federal Reserve and then customized per borrower, based on credit score, down payment, property type and points the buyer pays to lower the rate.
Multiple Listing Service (MSL): A database where real estate agents list properties for sale.
Origination fee: A fee, charged by a broker or lender, to initiate and complete the home loan application process.
Piggyback loan: A combination of loans bundled so as to avoid private mortgage Insurance. One loan covers 80 percent of the home’s value, another loan covers 10 to 15 percent of the home’s value and the buyer contributes the remainder.
Principal, interest, property taxes and homeowners insurance (PITI): The components of a monthly mortgage payment.
Private mortgage insurance (PMI): A fee charged to borrowers who make a down payment that is less than 20 percent of the home’s value. The fee, 0.3 percent to 1.5 percent of the yearly loan amount, can be canceled, in certain circumstances, when the borrower reaches 20 percent equity.
Points: Prepaid interest owed at closing, with one point representing one percent of the loan. Paying points, which are
Pre-approval: A thorough assessment of a borrower’s income, assets
Pre-qualification: A basic assessment of income, assets and credit score to determine what, if any, loan programs a borrower might qualify for. A real estate agent will request a pre-approval or pre-qualification letter before showing a buyer a home.
Property tax exemption: A reduction in taxes based on specific criteria, such as
Round table closing: All parties (the buyer, the seller, the real estate agents and maybe the lender) meet at a specified time to sign paperwork, pay fees and finalize the transfer of homeownership.
Seller’s market: Market conditions that exist when buyers outnumber homes for sale. Bidding wars are common.
Short sale: The sale of a home by an owner who owes more on the home than it’s worth (i.e. “
Special assessment: A fee charged by a condo complex HOA when cash on reserve is not enough to cover unexpected expenses.
Tax lien: The government’s legal claim against property when the homeowner neglects or fails to pay a tax debt.
Third-party review required: Verbiage included in a home listing to indicate that the lender has not yet approved the home for short sale. The seller must submit the buyer’s offer to the lender for approval.
Title insurance: Insurance that protects the buyer and lender should an individual or entity step forward with a claim that was attached to the property before the seller transferred legal ownership of the property or “title” to the buyer.
Transfer stamps: The form in which transfer taxes are paid by the home buyer. Stamps can also serve as proof of transfer tax payment.
Transfer taxes: Fees imposed by the state, county or municipality on
Under contract: A period of time (30 days or longer) after a buyer has made an offer on a home and a seller has accepted. During this time, the home is inspected and appraised and the title searched for liens, etc.
Underwriting: A process a lender follows to assess a home loan applicant’s income, assets, credit etc. and the risk involved in offering the applicant a mortgage.
VA home loan: A home loan partially guaranteed by the United States Department of Veteran Affairs and offered by private lenders, such as banks and mortgage companies.
VantageScore: A credit scoring model relied upon by lenders to make lending decisions. A borrower’s score is based on bill-paying habits, debt balances, age and variety of credit accounts and
Walk-through: A buyer’s final inspection of a home before closing.
Water certificate: A document that certifies that a water account has been paid in full. The seller must produce this certificate at closing.

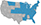 See Our National Coverage Map
See Our National Coverage Map